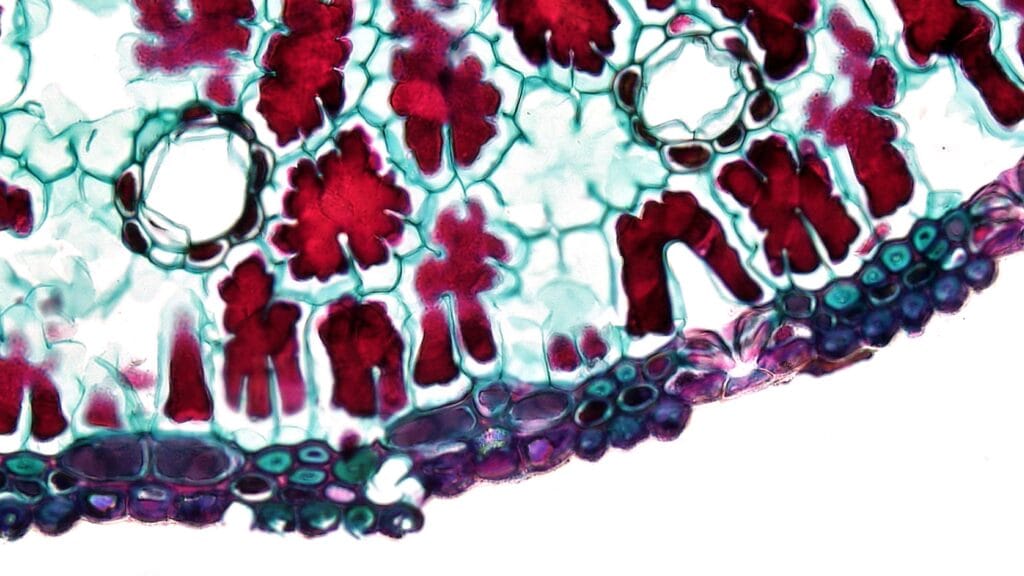
Introduction
The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Notes-Robert Hooke was the first to observe the Cell in the year 1665. Robert Hooke, the biologist, introduced the term cell for the first time in one of his publications, called Micrographia, and he declared that the cell is a box-like structure by watching through the lens. The word cell comes from the Latin word ‘cella’, which means small room. Before Robert Hooke, many scientists started their work on introducing the term cell.
One of them, like Anton Von Leewenhok he saw the cell first and he described the first live cell. He noticed that the cell contains the movements, and he noticed that the movement of a protist, like in sperm, bacteria, and red blood cells these is also known as the animolecules. Later the Robert Brown also discovered the term nucleus also. Paramecium, Amoeba are unicellular organisms and also have independent existence, and they are capable of performing the basic functions of life in nature. In life, the most important basic unit of life is the cell. Without the cell, life cannot exist.
Theory of the Cell: Fundamental Unit Of Life
Many botanists research the cell theory in various methods by their own knowledge, like;
- Matthias Schledian – He researched that plants contain different types of cells, for forming the plant tissues in the year 1838
- Theodore Schwann – He also stated that cells of all animals contain a thin layer called the plasma membrane in the year 1839; he also noticed that all product cells are composed in a unique type of way in plant and animal body cells
- Later, Schleiden and Schwann both started research on the cell theory. They both stated that the fundamental unit of all living things is the ‘cell’, with that all living organisms survive in nature
- Rudolf Virchow- he noticed that the cells and new cells are dividing and forming the pre-existing cells, and also developed the Schleiden and Schwann theory

The Cell Theory Exceptions
- The cellular machinery doesn’t recognize Viruses, and they are later known as organisms.
- The sieve tube cells and Red blood cells live by their own time
- The nuclear membrane and prokaryotic cells lack the genetic material of the cell theory
- The algae and fungi formed by protoplasm contain a number of nuclei example, Vaucheria in algae form and Rhizopus in fungi form.
Cell Size, Shape, Life Span
- All the cells do not have the same shape, size, and also the same life span, but it depends on the nature of the cells.
- Their activities are also different in their life span in different cells.
- In parenchyma cells, the cells are in irregular shapes in plants, and also different plants perform different types.
- The Red blood cells of humans are biconcave and circular in shape
- In the ameba, the White blood cells travel through the capillary walls
- In plants, the guarding cells are mostly like in dumb-bell shaped, and some are bean-shaped in size
- Mycoplasmas it is present in Prokaryotic organisms and can be seen as the smallest cells
- In Acetabularia, the algae can be measured at only 7.0 meters in diameter
- Ostrich contains a single largest cell in its egg it.
Types of cells
- Basically, cells can be divided into two types: Eukaryotic cells and Prokaryotic cells
- Prokaryotic cells: It is present in blue-green algae, bacteria, E. coli, and Mycoplasma
- Bacteria: I is present in Monococcus, diplococcus, tetra cococuss, Spirillum, Vibrio, Bacillus, etc..
- Flagella: Monotrichous, Aritrichos, peritrichos, Amphitrichous, Lophotrichous
Wall of the cell- Fundamental Unit of Life
- The cell wall protects and guards the cell in every organism, like bacteria, and other harmful substances
- Peptidoglycan is the most important cell wall of all eubacteria and cyanobacteria cells naturally
- It determines the shape and structure of the cell, and it supports the strength to make the cell smooth
- Mycoplasma, all prokaryotes contain cell walls to strengthen the cells
- The cell wall acts as a strong structural support and to prevent the cells from bacteria and other viruses
- In the matrix, it contains gums, resins
- It is mainly made up of cellulose
- The cell wall can be seen in plant cells, bacteria, and a few fungi
- The cell wall is a non-living thing and has with permeable membrane
Functions Of the Cell Wall
- It plays a mechanical support to the cell
- It maintains a definite shape to the cell
- It protects all the inner membranes of the cell components
- It stops the unwanted viruses and bacteria from entering the cells
- It leads to playing various activities to make the cell healthier
Plasma Membrane
- After the part of the cell wall, the plasma membrane can play a major role in developing the cell
- In all prokaryotic cells, mainly the plasma membrane is present inside the cell
- The plasma membrane is different in prokaryotic cells and Eukaryotic cells
- Basically, the plasma membrane is made up of due to only Phospholipid layers
- The plasma membrane acts like a boundary of the cell to guard from bacteria
- Mostly, in cells, the plasma membrane is made up of proteins and phospholipids
- It can be seen in all cells
- It is a living and consists of semi-permeable
Cytoplasm- Fundamental Unit Of Life
- In the cell, the cytoplasm can be seen in like fluid-like structure
- In prokaryotic cells, the cytoplasm is not seen
- In ribosomes and other bodies, the cytoplasm can be seen like in granular shapes
- In some cells, the cytoplasm can also be present due to its structural functions
- The cytoplasm contains nucleotides, vitamins, and other organelles
- It plays various chemical actions in the cell to survive, the nutrients and metabolites, and enzymes, etc
Golgi Complex
- Camilo Golgi conducted experiments related to the Golgi complex in the year 1898
- In Eukaryotic cells, the Golgi complex is present in all cells except the RCBS of mammals and other cells
- In animal cells, it can be present in 3-7 cells, and in plant cells, it can be present in 10-20 Golgi complexes
- Golgi discovered these complexes in the nucleus of the nucleus of owl
Flagella
- Many bacterial cells contain flagella, which can be present in motile and non-motile forms
- In bacteria, the flagella can be seen in a wide range of numbers of cells
- Flagellum can also be divided into three parts;
- Filament- It is the long portion in length in bacteria. It extends the surface of the cell.
2. Hook- It can be seen as a curved shape, and it can be present in the inside cell
3. Basal body- It is made up of four rings, and it rotates the flagella to move in all directions
Vacuoles- Fundamental Unit Of Life
- In the cytoplasm, it contains fluid-filled vesicles named Vacuoles
- The vacuoles are fewer in animal cells, larger in plant cells
- It functions exchange of gases between the cytoplasm and fluids
- It contains four types of Vacuoles; They are
- Sap vacuoles
- Food Vacuoles
- Contractile Vacuoles
- Air Vacuoles
Mitochondria
- Many biologists research the mitochondria also, like Kolliker, Benda, Altamann, Hoogeboom, etc.
- Mitochondria are also called Chondrosomes and plasmasomes
- It is found in all cells except in prokaryotes, some RBCs, etc
- Mitochondria are present in cells in spherical, oval, cylindrical, pear in pear-shaped forms based on their structural functioning
- It depends on the activities of the cell and the structure of the cell
- Mitochondria contain DNA and RNA and 70s ribosomes, and other components of the proteins
- During the procedure of fusion, the mitochondria can easily be divided into regular parts
- The power cell of the cell is the Mitochondria
- It transfers the powers and energy to perform all the functions, It also helps in the Oxidation of carbohydrates and fats